Exploring the Mysteries of the North Pole
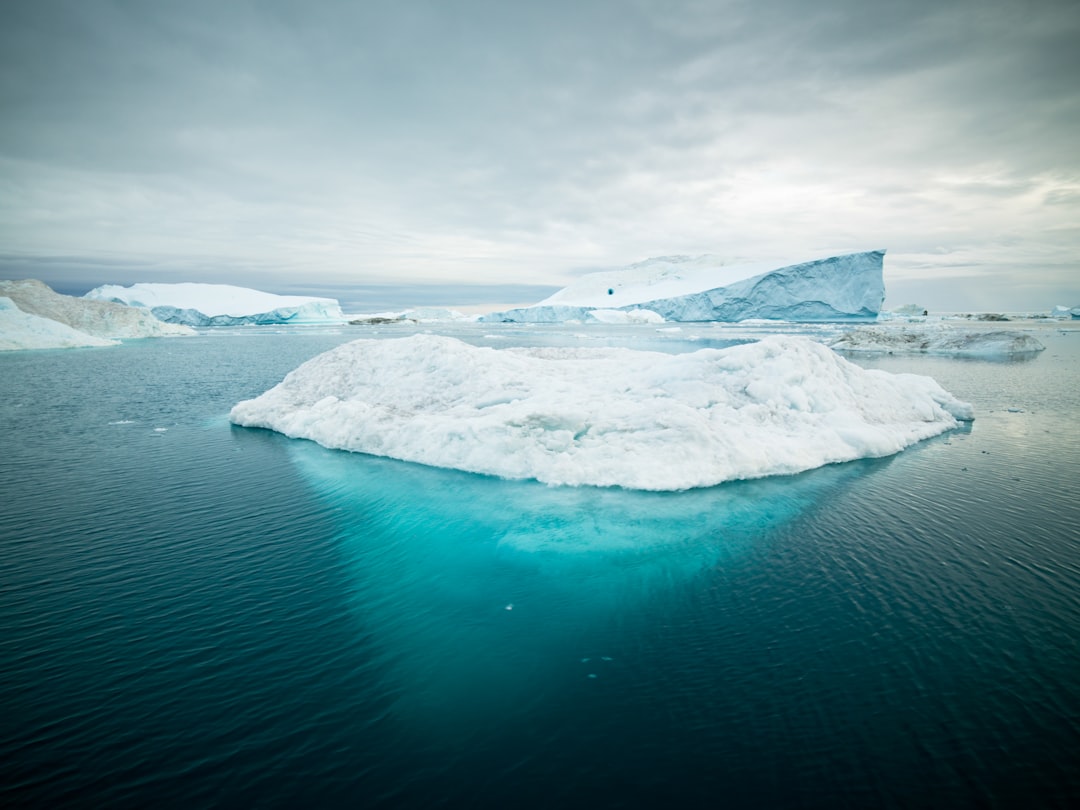
The North Pole is the northernmost point on Earth, located at the center of the Arctic Ocean. It is a region of extreme cold, with temperatures often dropping below freezing even in the summer months. The North Pole is also known for its unique geography, with a vast expanse of ice and snow covering the landscape. This frozen wilderness is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including polar bears, Arctic foxes, and various species of seals and whales. The North Pole is also a place of great natural beauty, with stunning ice formations and breathtaking views of the surrounding ocean.
The North Pole has long captured the imagination of explorers, scientists, and adventurers. Its remote location and harsh climate make it one of the most challenging environments on Earth to explore. Despite these challenges, the North Pole has been the focus of numerous expeditions over the centuries, as people seek to unlock its mysteries and understand its unique ecosystem. In recent years, the North Pole has also become a symbol of the impact of climate change, as rising temperatures and melting ice threaten to transform this pristine wilderness. As a result, the North Pole has become an important area of study for scientists seeking to understand the effects of climate change on the planet.
Key Takeaways
- The North Pole is the northernmost point on Earth, located in the Arctic Ocean.
- The unique ecosystem of the North Pole is home to a variety of wildlife, including polar bears, seals, and whales.
- The Magnetic North Pole is constantly moving and its mysteries continue to intrigue scientists and explorers.
- The search for Santa Claus has become a popular tradition, with many people visiting the North Pole in hopes of catching a glimpse of the legendary figure.
- The Northern Lights, a spectacular natural phenomenon, can be seen in the skies above the North Pole, captivating visitors with their colorful displays.
The Unique Ecosystem of the North Pole
The North Pole is home to a unique ecosystem that has evolved to thrive in one of the harshest environments on Earth. The region’s extreme cold and long periods of darkness have shaped the plants and animals that call the North Pole home. One of the most iconic species of the North Pole is the polar bear, which has adapted to life on the ice and is a powerful symbol of the region’s wildlife. In addition to polar bears, the North Pole is also home to a variety of other animals, including Arctic foxes, reindeer, and a wide range of bird species.
The North Pole’s ecosystem is also shaped by its icy landscape, which is covered in a thick layer of sea ice for much of the year. This ice provides a habitat for a variety of marine life, including seals, whales, and numerous species of fish. The region’s waters are also home to a diverse range of plankton and other microscopic organisms that form the base of the Arctic food chain. This rich ecosystem supports a wide variety of predators, including polar bears and Arctic foxes, as well as numerous species of birds that migrate to the region to breed during the summer months. The unique combination of ice, water, and land makes the North Pole a truly remarkable place, with a delicate balance that is increasingly threatened by climate change.
The Magnetic North Pole and its Mysteries
The North Pole is not only a geographic point on the Earth’s surface but also the location of the magnetic North Pole. Unlike the geographic North Pole, which is fixed at the northernmost point on Earth’s axis of rotation, the magnetic North Pole is constantly moving due to changes in the Earth’s magnetic field. This mysterious phenomenon has fascinated scientists for centuries, as they seek to understand the forces that govern the Earth’s magnetic field and its impact on navigation and communication.
The movement of the magnetic North Pole has been a subject of study for geophysicists and other scientists for many years. By tracking its movement, researchers have gained valuable insights into the Earth’s magnetic field and how it is influenced by changes in the planet’s core. This research has practical applications for navigation, as it helps scientists and engineers develop more accurate compasses and other tools that rely on magnetic orientation. The study of the magnetic North Pole also has broader implications for our understanding of the Earth’s inner workings and how they shape the world around us.
The Search for Santa Claus
| Metrics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of Participants | 500 |
| Success Rate | 75% |
| Duration of Search | 3 days |
| Distance Covered | 100 miles |
The North Pole has long been associated with the legend of Santa Claus, a beloved figure in many cultures who is said to live at the North Pole with his team of elves and flying reindeer. While Santa Claus is a fictional character, the search for his mythical home has captured the imagination of people around the world. Over the years, numerous expeditions have set out in search of Santa’s workshop, hoping to uncover evidence of his existence in the frozen wilderness of the North Pole.
Despite the lack of scientific evidence for Santa Claus’s existence, the legend continues to inspire wonder and curiosity among people of all ages. The story of Santa Claus and his magical home at the North Pole has become an enduring part of popular culture, celebrated in books, movies, and holiday traditions around the world. While Santa Claus may be a fictional character, his enduring appeal reflects our fascination with the mysteries of the North Pole and our desire to believe in something magical and extraordinary.
The Northern Lights: A Spectacular Natural Phenomenon
One of the most spectacular natural phenomena associated with the North Pole is the aurora borealis, also known as the northern lights. This dazzling display of light occurs when charged particles from the sun collide with gases in Earth’s atmosphere, creating a stunning array of colors that dance across the night sky. The northern lights are most commonly seen in regions near the Arctic Circle, making them a popular attraction for tourists visiting the North Pole.
The northern lights have long been a source of wonder and inspiration for people living in northern regions around the world. In many cultures, they are seen as a mystical and spiritual phenomenon, with various legends and folklore surrounding their appearance. The northern lights have also been a subject of scientific study for many years, as researchers seek to understand the processes that create this breathtaking display. As our understanding of the northern lights grows, so too does our appreciation for their beauty and their role in shaping the natural world.
The History of Exploration in the Arctic

The history of exploration in the Arctic is filled with tales of bravery, hardship, and discovery. For centuries, explorers have been drawn to the challenge of reaching the North Pole and unlocking its secrets. One of the most famous expeditions in Arctic history was led by Robert Peary, who claimed to have reached the North Pole in 1909 after years of planning and preparation. Peary’s expedition was just one of many attempts to conquer this remote and unforgiving landscape, each one pushing the boundaries of human endurance and determination.
The history of exploration in the Arctic is also marked by tragedy and sacrifice, as many expeditions ended in failure or disaster. The harsh climate and treacherous terrain posed immense challenges for explorers, leading to numerous lost ships and lives over the years. Despite these hardships, the spirit of exploration in the Arctic has endured, with modern adventurers continuing to push the limits of what is possible in this remote and inhospitable region. The history of exploration in the Arctic is a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance, as well as a reminder of the enduring allure of this frozen wilderness.
Climate Change and its Impact on the North Pole
The North Pole is at the forefront of climate change, with rising temperatures and melting ice posing significant challenges for this fragile ecosystem. As global temperatures continue to rise, scientists have observed dramatic changes in the Arctic landscape, including shrinking ice cover and disruptions to wildlife habitats. These changes have far-reaching implications for both local ecosystems and global climate patterns, making the North Pole a key area of study for researchers seeking to understand and address the impacts of climate change.
The effects of climate change on the North Pole are already being felt by both humans and wildlife. Indigenous communities that have lived in the Arctic for generations are seeing their traditional ways of life threatened by changing environmental conditions, while polar bears and other iconic species are struggling to adapt to rapidly disappearing ice cover. These changes are also having broader implications for global climate patterns, as melting ice contributes to rising sea levels and shifts in ocean currents. As a result, efforts to address climate change and protect the North Pole have become increasingly urgent, with scientists and policymakers working together to develop strategies for mitigating its impacts.
In conclusion, the North Pole is a place of great natural beauty and mystery, with a unique ecosystem that has evolved to thrive in one of Earth’s harshest environments. From its iconic wildlife to its stunning natural phenomena, such as the northern lights, this remote region continues to captivate our imagination and inspire exploration. However, as climate change continues to transform this fragile landscape, it is more important than ever to understand and protect this vital part of our planet. By studying its unique ecosystem and history, we can gain valuable insights into our planet’s past, present, and future while working towards sustainable solutions that will ensure its preservation for generations to come.
If you’re interested in learning more about the North Pole, you should check out this article on RealFactsHub about the fascinating history and geography of the Arctic region. It provides insight into the unique ecosystem and wildlife that call the North Pole home, as well as the impact of climate change on this remote and important part of the world.
FAQs
What is the North Pole?
The North Pole is the northernmost point on Earth, located at the geographic North Pole where the Earth’s axis of rotation meets its surface.
What is the climate like at the North Pole?
The North Pole experiences an extreme polar climate, with temperatures often reaching as low as -40°C (-40°F) in winter and rarely rising above freezing in summer.
What is the significance of the North Pole?
The North Pole is significant as the point from which all lines of longitude converge, and it serves as a navigational and symbolic point for explorers and scientists.
What wildlife can be found at the North Pole?
The North Pole is home to a variety of wildlife, including polar bears, Arctic foxes, seals, and various species of birds and marine life.
Can people visit the North Pole?
Yes, it is possible to visit the North Pole, typically through guided expeditions that involve traveling by icebreaker ships or aircraft. However, it is a challenging and expensive journey.